Everllence Powers Boston’s District Energy Utility with Largest Steam Heat Pump
Key Takeaways
- Everllence and Vicinity Energy's project will install the largest steam heat pump, decarbonizing Boston's district heating network using renewable electricity and river thermal energy.
- The system will generate 50 metric tons of steam/hour, serving over 70 million sq. ft. of building space, operational by 2028.
In addition to installing the world’s largest steam heat pump at Kendall Station, Everllence will include a dynamic process simulation and digital twin of the system.
In collaboration with Vicinity Energy, Everllence began an industrial-scale heat pump project to install the
“Execution of this project makes Vicinity’s vision of decarbonizing cities at scale a reality,” said Kevin Hagerty, CEO at Vicinity Energy. “Powered by renewable electricity to safely and efficiently harvest energy from the Charles River, this represents advancement in electrification for U.S. district energy systems demonstrating how heat pump technology can be deployed at scale to decarbonize cities. It enables immediate, scalable carbon reductions without the need for costly and time-intensive new electrical infrastructure in Greater Boston. We are establishing the blueprint of how to decarbonize a U.S. city and will be installing similar electrification technologies at our district energy systems across 12 U.S. cities.”
Despite being harnessed to generate renewable electricity, the river water is continuously returned to its source. Branded as eSteam, the decarbonized steam will be transported to homes, businesses, and medical and educational institutions through Boston’s current district heating network. This replaces natural gas-fired boilers without requiring expensive infrastructure modifications, highlighting the larger role of industrial-scale heat pumps in addressing grid stability, energy affordability, and natural gas dependence.
“The heating sector still drives a major portion of global CO2 emissions, and the energy transition simply cannot succeed without decarbonizing heat,” said Uwe Lauber, CEO at Everllence. “District heating remains one of the most efficient and sustainable ways to deliver thermal energy to commercial and industrial users. With this latest agreement, we are taking a step forward with Vicinity to bring our mega heat pump technology to the U.S. market. Together, we are demonstrating how district energy systems can shift away from fossil fuels while maintaining resilience and performance.”
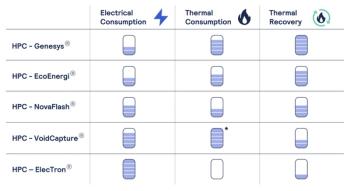
Most U.S. district energy networks operate with steam, which presents certain challenges and opportunities for decarbonization. Everllence’s system combines a vapor compression cycle with steam compression, generating high-pressure steam up to 50 bar and over 300 °C. To achieve this pressure and temperature, the system integrates two multi-shaft integrally geared compressors: type RG40-8 for refrigerant compression and type RG63-6 for steam compression.
The project scope also includes a dynamic process simulation, allowing the complete heat pump process to be modeled and subjected to numerous transient operating scenarios in real time. Additionally, Everllence delivered an in-depth digital twin of the system, enabling stress testing of the compressors’ performance in the engineering phase. These software-based solutions allow the installation to be operated under optimal conditions up to and beyond the first service hour.
Seawater Heat Pump
In early December 2024, Everllence’s
Newsletter
Power your knowledge with the latest in turbine technology, engineering advances, and energy solutions—subscribe to Turbomachinery International today.