Turbo Expo 2023: OEMs Innovate for a Greener Future
On Wednesday, June 28 at Turbo Expo 2023, a panel of OEMs presented at the Pathway Forward: Future Gas Turbine Products & Technologies–OEM Perspective session.
On Wednesday, June 28 at Turbo Expo 2023, a panel of OEMs discussed their innovations and different applications of gas turbines and machinery in the future of energy systems.
Caroline Marchmont, Director, R&D Execution at Ansaldo Energia, said the next major milestone in the industry’s pathway to net zero is moving gas turbines to hydrogen, which is expected to happen sometime between 2030-2040. Further, “Once we replace the coal plants, that will reduce the CO2 emissions for that plant by about half,” she said.
Another factor to consider is the sustainability of existing assets.
“What can we get out of what we already have?” Marchmont said. “And how can we reuse technology as well as advancing technologies to improve on the existing assets?” And this includes adapting existing technologies to support renewables.
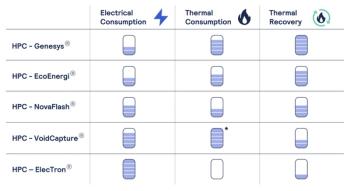
Improving existing assets or retrofitting can be tricky, but with its MXL3, Ansaldo Energia upgraded the first two stages of the low-pressure turbine. The company already has a combustor that's capable of 45% hydrogen, and it’s updated the compressor to optimize the performance and better match the turbine. With all of this, it gets up to 35 MW and 1.6% combined-cycle efficiency improvement.
Marchmont said this, among other advancements/upgrades, is possible through collaboration and cooperation, which was stressed by many presenters throughout this week’s conference.
Dan Reitz, Manager of Product and Technology Strategy at Solar Turbines, outlined the company’s strategic plan to reduce emissions and enhance the use of alternative fuels. Reitz mentioned how the company is prioritizing four areas: operational efficiency, methane abatement, hydrogen fuel flexibility, and carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS).
Solar Turbines is leveraging a digital platform to optimize operational efficiency and has developed an integrated mobile solution for methane abatement. In terms of hydrogen fuel, the company is expanding its capacity in collaboration with several energy companies. The aim is to gradually mix hydrogen into their products up to 100%.
In terms of CCUS, Solar Turbines is focusing on technology to enhance CO2 concentration in the exhaust stream, which will make the capture process more cost-effective. They're also testing a pilot project in partnership with Chevron. Despite uncertainties in the energy landscape, Solar Turbines remains optimistic about the potential of market-driven solutions and legislative incentives to advance low-carbon goals.
Michael Hughes, Hydrogen Combustion Technology Integration Leader at GE Vernova, stressed the role of gas turbines in transitioning toward renewable energy. The push for decarbonization has prompted a shift toward efficient natural gas plants, but the role of these plants is evolving. Hughes predicts they'll increasingly serve as flexible power sources—for example, starting multiple times a day or load-following as required. Pertinently, Hughes stated that gas turbine core components will not need extensive changes to accommodate these alternative fuels like hydrogen or ammonia.
According to Hughes, GE has developed combustors for hydrogen fuels, and it is confident about the potential of axial fuel staging systems in this application. He touched on how the company is collaborating with Shell to create a 100% hydrogen-capable E-class system. Further, a Department of Energy (DOE)-funded program is in place to develop a similar system for H-class turbines. Hughes acknowledged challenges such as maintaining operability across a range of hydrogen levels and ensuring flashbacks don't occur. The aim is not just to transition to renewable fuels, but to do so in a way that integrates seamlessly with existing infrastructure and operations.
Newsletter
Power your knowledge with the latest in turbine technology, engineering advances, and energy solutions—subscribe to Turbomachinery International today.