Turbomachinery Digitalization, AI, and Smart Maintenance in 2025
Key Takeaways
- Digitalization and AI are transforming turbomachinery operations, enhancing real-time data capture, remote monitoring, and proactive management across sectors.
- AI optimizes design and operations, enabling predictive diagnostics and performance enhancement, while addressing workforce gaps through automation.
Digital tools, AI, and predictive maintenance are reshaping turbomachinery and driving gains in reliability, efficiency, and long-term asset performance in 2025.
The turbomachinery industry in 2025 continues to integrate digital technologies, AI, and advanced maintenance strategies into the design, operation, and service of compressors, turbines, and related rotating equipment. A combination of industry demand for greater reliability, decarbonization targets, and workforce transitions has accelerated digital transformation across OEMs, service providers, and end users.
Digitalization as Foundation
Digitalization is reshaping turbomachinery engineering and operations. Companies are increasingly deploying Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, cloud-based monitoring systems, and advanced analytics tools to capture and process high volumes of operational data in real time. These systems expand on traditional supervisory control and data acquisition and distributed control systems, enhancing visibility into machine health and performance across global fleets.
Digital tools also support remote monitoring and control, enabling operators to manage assets from centralized locations. OEMs and solution providers are investing in digital ecosystems that combine secure connectivity with scalable data services, facilitating proactive operational management across energy, petrochemical, and industrial sectors.
AI in Design and Operations
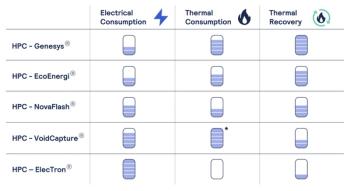
AI’s role in the turbomachinery industry spans multiple phases of the asset lifecycle, from design and manufacturing to operation and service. At the 2025
In operations, AI-equipped software and controls help make sense of vast data streams and automate routine tasks. AI models embedded in control systems can detect early signs of performance degradation, trigger alerts, and even adjust control responses to maintain output stability. By automating these processes, operators are better positioned to manage larger portfolios of assets with smaller teams, addressing workforce gaps left by retiring technical staff.
Research in manufacturing digitalization confirms AI’s importance in enabling real-time modeling and decision support, where predictive models function as intelligent collaborators that augment human expertise while optimizing process parameters and operational outcomes. These capabilities are key to preparing for future smart manufacturing paradigms.
Smart Maintenance and Predictive Strategies
Smart maintenance—often referred to as predictive or condition-based maintenance—has become a strategic priority in 2025. Traditional reactive maintenance, which responds to failures after they occur, is being supplanted by approaches that anticipate issues before they lead to unplanned outages. The global services market for
A range of technologies illustrates this trend. Beyond conventional vibration and thermal sensing, electrical signature analysis platforms are gaining attention for their ability to continuously capture high-resolution electrical data and deliver actionable predictive insights. Such systems convert raw waveform data into health fingerprints for pumps, compressors, and turbines, enabling engineers to anticipate mechanical or process-related issues far earlier.
Digital twin technology—virtual replicas of physical systems—further strengthens predictive maintenance. By integrating real-time sensor data with simulation models, digital twins allow engineers to monitor the evolving condition of an asset, optimize maintenance schedules, and test scenarios without interrupting live operations. A growing share of turbomachinery installations now incorporates digital twins, supporting more informed maintenance decisions while simulating performance under different conditions.
Operational Efficiency and Decarbonization
The convergence of digitalization, AI, and smart maintenance is closely tied to broader industry goals, including
In sectors such as renewables and LNG, reliable turbomachinery performance is critical. Predictive technologies help ensure near-continuous operation of critical assets, reducing reliance on backup systems during downtimes and supporting cleaner energy production. Decarbonization drives ongoing investment in digital tools, as operators seek to meet emissions targets while maintaining competitive costs.
Challenges and Industry Adoption
Despite the clear benefits, the adoption of digital and AI-driven maintenance techniques faces several hurdles. Integration with legacy systems, data quality issues, and workforce preparedness are recurring concerns. Operators must balance investment in new technologies with practical considerations about implementation complexity and return on investment. Some practitioners caution that not all AI systems deliver actionable insights, emphasizing the need for solutions that integrate domain expertise and transparent model behavior. Independent assessments suggest that explainable AI and prescriptive maintenance—systems that recommend specific actions—are poised to gain traction as maturity grows.
Moreover, the digital skills gap in engineering and maintenance remains a barrier. Companies are investing in training and workforce development to ensure that technicians and engineers can effectively use advanced analytics platforms and interpret AI outputs. Collaboration between OEMs, service providers, and end users is increasingly seen as essential to successful adoption.
“One of the defining challenges today is the Great Crew Change, where people with decades of experience and expertise are retiring in mass—being replaced by fewer people with less operational experience,” said Shun Yoshida – Engineering Manager, HMI Software at Compressor Controls Corp. by Honeywell. “This is while they are asked to manage energy efficiency, reliability of aging assets, and sustainability goals. They have a difficult job ahead in maintaining and even improving assets with less collective experience available in the team.”
Outlook for 2026 and Beyond
Looking ahead, industry analysts forecast continued growth in digital and AI-enabled maintenance solutions. As data infrastructures mature and AI models become more sophisticated, turbomachinery operators are expected to accelerate their shift from reactive to predictive and, ultimately, autonomous maintenance frameworks. Digital twin adoption is likely to expand further, along with advances in real-time analytics, edge computing, and integrated control systems.
“The turbomachinery maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) market is worth over US$30 billion and is expected to grow significantly in the upcoming decade,” according to Frank Ma, President of JFMA Consulting LLC. “These needs are extending the operational life of existing turbomachinery fleets and driving growth for MRO services.”
The turbomachinery sector’s digital transformation reflects broader shifts in industrial engineering toward smarter, more efficient, and more resilient operations that leverage data as a strategic asset. While challenges remain, the trajectory points toward a future where digitalization and AI are standard components of turbomachinery performance and maintenance strategies.
Newsletter
Power your knowledge with the latest in turbine technology, engineering advances, and energy solutions—subscribe to Turbomachinery International today.